Super User
期刊連結
註:僅限台大校園網路範圍使用(校外須使用VPN連線)
研究室簡報下載
研究室簡介
| Links | Director |
| 雲與氣候研究室 | Professor Chung-Hsiung, Sui 隋中興 Ph.D. University of California, Los Angeles, 1984. 33663908 |
| 動力與模擬研究室 | Professor Hung-Chi Kuo郭鴻基 Ph. D. Colorado State University, 1987. 33663910/23671291 |
| 雲與氣膠研究室 | Professor Jen-Ping Chen 陳正平 Ph.D. Pennsylvania State University, 1992 33663912/23633317 |
| 颱風動力研究室 | Professor Chun-Chieh Wu吳俊傑 Ph.D., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1993. 33663913/23632303 |
| 衛星遙測研究室 | Professor I-I, Lin 林依依 Ph.D. University of Cambridge, UK, 1995. 33663917/23660418 |
| 中尺度暨地形降水研究室 | Professor Cheng-Ku Yu 游政谷 Ph.D. National Taiwan University, 1995. 33663902 |
| 對流及降水實驗室 | Professor Ming-Jen Yang 楊明仁 Ph.D. University of Washington, 1995. 33663900 |
| 大氣測計研究室 | Professor Po-Hsiung Lin 林博雄 Ph.D. National Taiwan University,1996. 33663916 |
| 大氣化學實驗室 | Professor Hui-Ming, Hung 洪惠敏 Ph.D. California Institute of Technology, 2000. 33663919 |
| 雲動力模擬研究室 | Associate Professor Chien-Ming Wu 吳健銘 Ph.D. University of California, Los Angeles, 2008. 33663905 |
| 陸地水文氣候及衛星遙測研究室 | Associate Professor Min-Hui Lo 羅敏輝 Ph.D. University of California, Irvine, 2010. 33663918 |
| 大氣環境研究室 | Associate Professor Wei-Ting Chen 陳維婷 Ph.D. California Institute of Technology, 2009. 33663914 |
| 氣候動力與全球變遷研究室 | Associate Professor Yen-Ting Hwang 黃彥婷 Ph.D. University of Washington, 2013. 33663904 |
| 極地氣候研究室 | Assistant Professor Yu-Chiao Liang 梁禹喬 Ph.D. University of California, Irvine, 2018. 33663907 |
博士班資格考核
1. 博士班學位考試分為三部分:
(1) 年度考核和資格考
(2) 預備口試
(3) 論文口試
2.年度考核和資格考
(1) 博士班學生於入學後三個月內,須成立博士學位候選人資格考核委員會,負責博士班學生之選課建議、年度考核和資格考。
(2) 資格考核委員會由五人組成,指導教授為當然委員並擔任召集人,委員名單由指導教授推薦二人,試務和學術委員會聯合推薦二人,經所長同意後聘任之。委員應具備學位授予法認定可擔任學位考試委員之資格,由本校專任助理教授以上教師擔任為原則,亦得由與該博士學位候選人研究方向有關之合格校外專任助理教授(或同等級人員)以上或本校合聘或兼任助理教授以上之教師擔任。委員名單需更動時亦同。
(3) 每位博士班學生每學年應接受資格考核委員會一次年度考核,考核項目包含專題討論的報告、修課及研究進展。考核應於每學年第二學期期末考完畢後一個月內之前完成。所長於彙整博士班學生專題討論報告時各出席教師之評分及評論後,提供考核委員會年度考核的參考。
(4) 年度考核結果分通過和不通過,未接受年度考核則視同不通過,修業年限內未通過考核達二次者,得令退學。
(5) 考核後,資格考核委員會應提供受考核學生研究或修課改進之建議。
(6) 博士班學生於入學三年內,須通過資格考。資格考由考核委員會出題,並決定是否通過之。資格考得與同學年度之年度考核合併舉行。
(7) 資格考結果分通過和不通過。未通過資格考者,得於6個月後再進行第二次資格考。未通過資格考達兩次者,得令退學。
(8) 學生因特殊情況(如懷孕、傷病)而未能於上述期間內完成年度考核或通過資格考者,得經指導教授同意後提出申請,並經本系試務委員會同意後可延後辦理其年度考核與資格考至多一年。
(9) 博士班學生可以一篇已發表(或已被接受發表)大氣科學相關領域之第一作者SCI-Extended論文或不低於第二作者之SCI論文(該論文作者單位地址須註明為本系)提出免試申請,經考核委員會認定通過,即視為資格考核通過。該論文須為碩士畢業後之研究成果。免試申請通過後,該申請論文不得再列為畢業所須之SCI論文。
3. 預備口試
(1) 每位學生需於入學後四年內通過以論文計畫書為主的預備口試(在職進修者,得延長一年)。預備口試由該生的資格考核委員會執行,若考核委員因研究進展有更動之需要,仍可依規定向系上提出申請。
(2) 口試結果分通過、不通過、條件式通過三種,條件式通過者給予在一年內重考一次之機會,不通過者得令退學。
4. 每位學生應於博士學位口試二星期之前提出論文初稿,由論文口試委員進行審查。
5. 學生通過資格考評和考核後,須有另外一篇大氣科學相關領域之第一作者SCI論文(該論文作者單位地址須註明為本系),始得申請博士學位考試。
6. 博士論文口試委員會由委員七人組成,包括校外委員三人與校內委員四人,於舉行預備考試前由指導教授提出建議名單,經所長同意後聘請之。
7. 核准逕行修讀博士學位之研究生,自轉入博士班起,至少應修業逾三學期,且連同碩士班至少修畢三十學分,始得申請博士班學位考試。
8. 其餘未列規定同本校教務章程
博士班修課規定
1. 博士班修業年限為二年至七年,逕行修讀博士學位者,自轉入博士班起,其修業年限依照前項規定辦理。
2. 本所博士班研究生必須修滿十八學分(不含畢業論文);修讀博士學位之研究生,自轉入博士班起,至少應修業滿二年,且連同碩士班至少修畢三十學分(不含畢業論文)。其必修課程如下:
(1) 由指導教授協助學生共同規劃一門適切之非指導教授開設之獨立研究。(繳交指導教授同意書)
(2) 專題討論至少應修二學年(2學期0學分,2學期1學分)共二學分。
3. 博士班專題討論報告規定:
l 博班學生在學生生涯中必須報告2次,且須安排在修「有學分」專題討論的學期。
l 除上述2次報告外,若博班生仍有意願報告,可安排在週四演講時段。
l 博班生每年仍須向考核委員會報告研究進展,完成年度考核相關規定。
l 博班口試可盡量安排在週二專題討論。由所有老師評分,並提出意見書供學生改進依據。
l 若遇特殊情況,如專題討論報告與畢業口試(或預備口試)合併時,得向學術委員會申請。經學術委員會同意,得將專題討論報告延後一學期,但每名博士班學生以一次為限。
4. 博士班畢業學分抵修規定:
l 博士班抵修以M、D字頭且5年內(不含義務兵役役期或懷孕)修過且未申請過抵修之大氣相關課程,且該成績需超過A- 或80分,特殊情況經指導教授與學術委員會核准者除外。
l 抵修學分不超過1/2畢業學分
l 專題討論及獨立研究相關課程不得作為申請抵修科目
l 請學生正面表列填寫該課程是否已抵修,經學術委員會認定
5. 博士論文(12學分)於博士學位論文考試之學期修習之。相關寫作資訊亦可參考台大寫作教學中心(http://www.awec.ntu.edu.tw/)
6. 博士生指導教授須以本系專任教師指導。
7. 自107學年度起入學之碩、博士班學生,以入學第一學年結束前修習完成至少六小時學術倫理課程(以下簡稱本課程)為原則。詳細內容請見「國立臺灣大學學術倫理課程修課實施要點」。
碩士班修課規定
1. 碩士班研究生修業年限為一至四年。
2. 本所碩士班研究生必需修滿二十四學分(不含畢業論文)。
3. 為因應碩士班甲、乙分組定義改變,本學年入學之碩士班新生必修課程如下:
(1)專題討論至少應修二年四學分
第一學年二學期皆零學分,需出席聽課;
第二學年二學期共四學分,除出席聽課外,上下學期需上台口頭報告。若下學期決定不參與院長獎評選同學,可以選擇在學期後段口頭報告或撰寫書面報告(在非碩班學生的專題演講中擇二撰寫書面報告,其內容包括摘要、演講相關資料整理、重要參考文獻)。學生須在碩二上學期期末結束前決定是否上台報告。
為鼓勵優秀學生提早畢業,學生可申請提前修有學分專題討論課程。但學生如未能提早畢業,則需補齊0學分之專題討論課程。相關辦法如下:
針對提前一學期(即修習一年半畢業)之學生
- 審核申請資格:優秀學生經指導教授同意,並於每年1月31日或7月31日前申請提前修習有學分之專題討論課程,申請者時需提出完整書面資料【包括碩士第一學期修課成績單及大學部成績單、未來修課計畫、未來研究計畫,及過去研究表現及成果,指導教授所提供彌封之推薦函(明確評估該生之修課與研究之表現與潛力)】,經學術委員會審核同意後始可先修有學分之專題討論;
針對提前二學期(即修習一年畢業)之學生
- 辦法同上(但無碩士第一學期修課成績單),唯需經系主任成立之審查委員會審核同意後始可先修有學分之專題討論。
(2)碩士班必修課程:本系開設「核心課程或M字頭課程」任選10學分(排除專題報告及獨立研究類課程),核心課程請見各學年度新生手冊,乙組入學同學另可選擇大學部部分必修課程(如下表)作為碩士班必修課程。原臺大大氣系畢業之學生於大學畢業時所修學群的必修課程不得作為碩士班必修課程。
(3)畢業學分需有至少二分之一為本系課程(包括與師大交換選課之課程,不含專題討論4學分)。
4. 入學前曾經修習過研究所科目(且成績在B-或70分以上)之同學,可以提出申請抵修(需經學術委員會審核通過始可抵免)。
5. 於大學超修之研究所課程(M字頭)可抵免畢業學分,但以9學分為限。
註:超修之研究所課程:扣除畢業學分(128學分),及系訂必選修(6學分)後,所多修之M字頭課程方可申請抵免。(106學年度後入學的大學生,其系訂必選修為10學分)
6. 各科學業成績以 B-為及格。
7. 每學期須至少選修本系課程一門。蓄意規避此規定者,所方得於下一學期不予簽章註冊。
8. 碩士論文(六學分)於申請碩士學位考試之學期修習之。相關寫作資訊亦可參考台大寫作教學中心(http://www.awec.ntu.edu.tw/)。或參考本系所開設之「初階科技英文寫作」、「進階科技英文寫作」
9. 大學非大氣科學(或大氣物理)系畢業者需補修「大氣科學概論」(但不計入畢業學分)。
10. 碩士班學生若欲跳修D字頭課程,需事先取得授課教師同意。
11. 碩士班學生修課應以本研究所開設之課程為原則,若修習其他系所課程須經學術委員會同意後,始可計入畢業學分。
(A) 申請時程:請於修課前向系辦提出申請。申請截止日:開學第一週結束前
(B) 外修課程須為本系沒有開設之課程(限為U、M、D字頭課程)
(C) 申請時請填寫欲外修之課程及原因,經指導教授同意後始可送件(表格請恰系辦領取)
12. 碩士班學生須於畢業前通過以下任一種規定,方得畢業:(A)通過全民檢中高級初試;(B)托福 550 分以上;(C)電腦托福213分以上或 TOEFL-iBT 79分以上;(D)IELTS 6級以上;(E)FLPT 英語測驗筆試各分項成績70分以上;(F) FCE B 級以上;(G) 獲得教育部參考名冊之英語系國家大學以上學位;(H)曾修習進階英語(一)、(二),且成績達C-(含)以上;(I) 通過研究生線上英語(一)、(二)
13.自107學年度起入學之碩、博士班學生,以入學第一學年結束前修習完成至少六小時學術倫理課程(以下簡稱本課程)為原則。詳細內容請見臺大的「國立臺灣大學學術倫理課程修課實施要點」
大學部修課規定

大學部教務相關規定
*同新生手冊內容,手冊所列為本系110學年度第一學期之各項規定與辦法,日後如有更動,以最新的規定為準。
一、選課程序
請同學逕自透過網路選課,詳細規定可參考學校註冊組規定。
二、修課規定
1. 大氣科學系必修課程共分二組學群,分別為天氣氣候學群,及大氣環境化學學群。本系最低畢業學分數為128學分,其中包括部訂共同必修+通識課程共24學分,系訂必修科目60學分,選修科目44學分。超修之共同必修學分,計入選修學分,但以不超過4學分為限。學生畢業前須符合上述其中一組學群之必修規定,方可畢業。
2. 本系必修科目擋修辦法
|
修課年級 |
本系必修科目 |
先修科目 |
|
大二 |
應用數學一 |
微積分甲下 |
|
大二 |
雲物理學 |
大氣熱力學 |
|
大三 |
天氣學一 |
大氣熱力學 |
|
大三 |
大氣動力學一 |
應用數學一 |
|
大三 |
大氣動力學二 |
大氣動力學一 |
|
大三 |
天氣學二 |
天氣學一 |
|
大三 |
天氣學實習二 |
天氣學實習一 |
|
大四 |
氣候學 |
大氣輻射學 大氣熱力學 大氣動力學一 |
附註:
A. 先修科目必須及格,始得修習本系之必修科目。
B. 如欲跳修必修課程,須具備下列條件:(1)平均成績須達全班成績前百分之二十,經學術委員會同意。或(2)經授課教師同意。
※ 應用數學一二、天氣學一二、天氣學實習一二、大氣動力學一二等科目,一皆擋修二。
※ 未選修天氣學者,不得選修天氣學實習。
3. 各年級每學期修習學分數限制:
一、二、三年級15-25學分,四年級 9-25學分。前一學期名次列所屬學系(組)該年級前百分之十之成績優異學生,或學業等第績分平均達三點九以上者,得修至三十一學分。
4. 學分抵免作業請依照學校時程辦理,經申請抵免通過後不得撤銷。
5. 其餘未列規定同本校教務章程。
6. 自八十六學年第二學期開始,理學院為獎勵學風,設有畢業生”院長獎”,本系大學部院長獎之給獎係於當年度畢業學生中,修習本系『核心課程』總成績在前10﹪以內者,評選為本系院長獎獲選學生。其中『核心課程』為:本系所開設之本系必修課程加上本系必選課程。另針對提前畢業之學生,仍保留其參與評定之資格。領院長獎同學須為學年畢業生,且需簽署確認書。如無法當學年畢業者,將取消該年院長獎資格。
三、必修與必選科目(110學年度入學適用)
|
|
大一上 |
大一下 |
大二上 |
大二下 |
大三上 |
大三下 |
|
學群共同必修 33學分 |
微積分1+2(4) |
微積分3+4(4) |
應用數學一(3) |
統計與大氣科學(2) |
天氣學一(2) |
|
|
天氣氣候必修 17學分 |
|
數值分析(2) |
|
應用數學二(3)
|
大氣動力學二(3) |
天氣學二(2) |
|
大氣環境化學必修 17學分 |
普化甲上+實(4) |
普化甲下+實(4) |
大氣化學(3) |
|
大氣物理化學(3) |
生地化循環與氣候(3)
|
|
天氣氣候必選群組 |
普物甲上(3)、普物甲下(3)、高等大氣動力學(3)、中尺度氣象學(2)、動力氣候學(3)、全球大氣環流(3)、氣候變遷科學(2)、陸地大氣交互作用(3)、雲動力學(3)、雲與環境(3)、地物流力(3) Research Track、Tool Track |
|
大氣環境化學必選群組 |
必選修課程(至少選 7 學分):有機化學(3)、分析化學(2-3)、物理化學(3)、應用數學二(3)、天氣學二+實習二(3) |
|
選修群組:普物上+普物實驗(4)、普物下+普物實驗(4)、數值分析(2)、地物流力(3)、雲動力學(3)、雲與環境(3)、陸地大氣交互作用(3)、生物氣象學(3)、大氣化學實作(2)、空氣汙染實作(2)、大氣動力學二(3)、氣候學(3)、氣候變遷科學(2) Research Track、Tool Track |
Research Track:大氣科學研究導論(2)、獨立研究(2)、學士論文(2)
Tool Track:大氣觀測實作(2)、天氣診斷專題一(2)、雲霧觀測實作(2)、大氣遙測(2)、雙偏極雷達專題(3)、氣候診斷(2)、氣候變遷議題實作(2)
四、研究軌道課程總覽
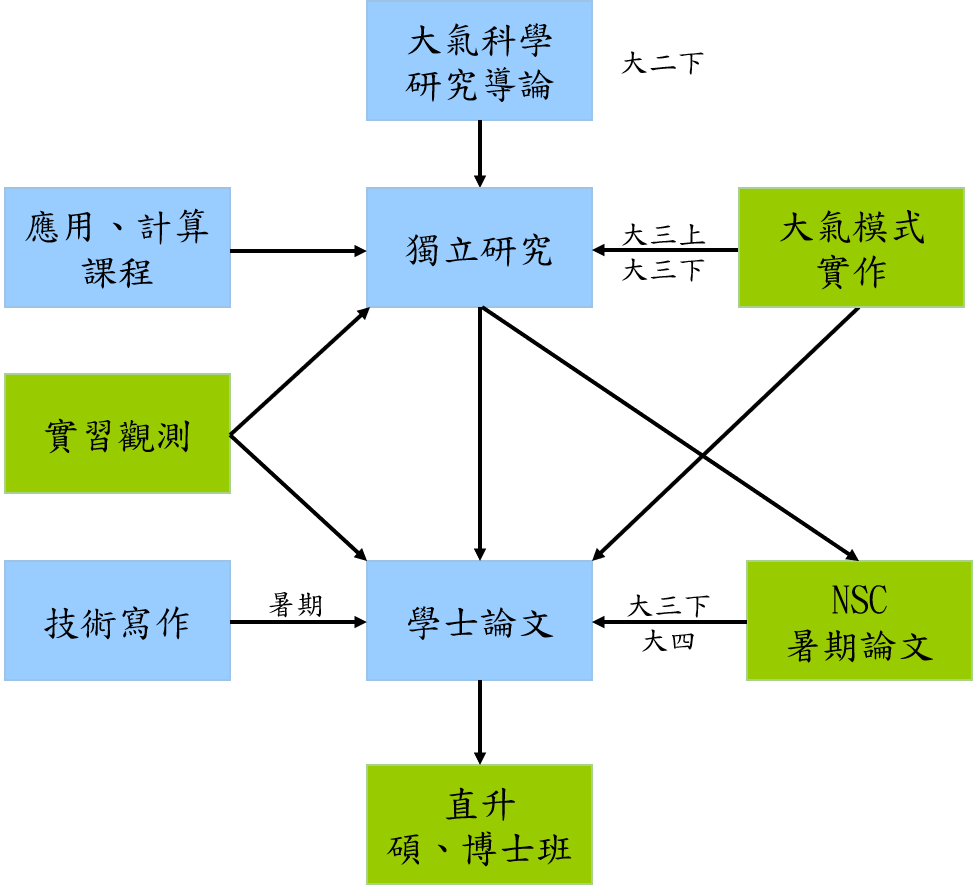
*獨立研究先修課程為大氣科學研究導論
*學士論文先修課程為獨立研究(適用93年度以後入學學生)
如欲跳修『獨立研究』、『學士論文』課程,須成績優良經授課教師或指導老師同意。
本學期課程
111學年度第一學期 上課時間表 V.5 111.8.24
|
星 期 |
一 |
二 |
三 |
四 |
五 |
|||||||||||||||
|
節次 |
科目 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
1 8:10 | 9:00 |
|
1大概(傑、輝、健、維、彥)B105 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
3大氣動力學二(郭)B105 |
3大氣動力學二(郭)B105 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
2 9:10 | 10:00 |
M深對流特論……(仁) A100 |
U空氣汙染導論(谷) A104 |
|
M機器學習在大氣熱力學的應用……(健) A104 |
||||||||||||||||
|
3 10:20 | 11:10 |
2應用數學一…(梁) B105 |
M科學寫作與發表01(谷) A100 |
34大氣科學研究導論 (輝、傑、健、彥) A104 |
M動力氣候學…… (隋) A108 |
M科學寫作與發表02(谷) A100 |
2大氣化學…(洪) B105 |
2雲物理學…………(平)B105 |
3天氣學一 ……… (仁、維)B105 |
M動力氣候學 (隋) A108 |
2應數一(梁) A104 |
2大氣化學…(洪) B105 |
M科學寫作與發表02(谷) A100 |
||||||||
|
4 11:20 | 12:10 |
|
|
M科學寫作與發表01(谷) A100 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
5 12:20 | 1:10 |
2大氣測計學……(博) B105 |
|
|
M全球大氣環流(彥) A104 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
6 1:20 | 2:10 |
U大氣環境概論(谷) A100 |
M大氣遙測(依) 共同105 |
|
MD 專 題 討 論 B105 |
|
專題演講保留時段…B105 |
3大物化(平) A104 |
|||||||||||||
|
7 2:20 | 3:10 |
M氣候變異與預測(盧、隋) A108 |
M雙偏極雷達專題(島、兆) A206 |
3天氣學實習一……… (仁、維)B105 |
M人為氣候變遷下的水文循環變化:陸地模式的應用(輝) A104 |
||||||||||||||||
|
8 3:30 | 4:20 |
1程式與科學計算…(維) B105 |
U空氣汙染導論(谷) A104 |
M混沌與可預報度(治) A100 |
|
U生命科學數學(郭) B105 |
物理海洋概論(楠) A104 |
M高等天氣與氣候動力(和) B105 |
3大氣物理化學…(平) A104 |
M混沌與可預報度(治) A100 |
|||||||||||
|
9 4:30 | 5:20 |
|
U大氣環境概論(谷) A100 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
10 5:30 | 6:20 |
U大氣程式實作(維) B105 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
大氣觀測實作(時地自訂)、地形降水獨立研究(時地自訂)
研究所課程
|
碩士班選修(M字頭) |
|||
|
課程名稱 |
教 師 |
學分 |
內 容 介 紹 |
|
動力氣候學 |
隋中興 |
3 |
本課程介紹大氣-海洋平均氣候與低頻震盪的特徵及動力過程,特別是熱帶多尺度波動。主要介紹ITCZ和年週期變化,熱帶氣旋與波動,季節內振盪、年際震盪(如厄爾尼諾 - 南方濤動,印度洋偶極子)、年代際變化。課程著重理論和概念模型的講授,以利學生理解觀測現象背後的物理機制。授課對象為具備大氣-海洋科學背景的大四及研究所學生。 |
|
大尺度雲與水汽過程 |
隋中興 |
2 |
Earth atmosphere is uniquely regulated by water cycle. It spans wide spatiotemporal spectrum and many layers of governing physics. Through interactions with energy cycle and circulation, the moisture and cloud of highly fluctuating nature exhibit surprisingly coherent large-scale structure. The corresponding convective-radiative processes relevant in climate oscillations of different scales are essential part of climate dynamic. |
|
高等數值天氣預報 |
楊明仁 |
3 |
This course will introduce the advanced applications of numerical weather prediction (NWP), mainly using the WRF model. The spectral and pseudospectral methods typically used in the global model and tropical cyclone studies will be discussed. Relaxation method used in solving the Laplace and Possion equations will be presented. Several methods for lateral boundaries used in regional models will be discussed. Class projects based on the material covered in this class will be assigned. Students taking this course are assumed to have the basic knowledge of finite-difference methods and numerical analysis. |
|
深對流特論 |
楊明仁 |
3 |
The physical and dynamical processes of deep cumulus clouds, which usually occur in mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), tropical cyclones and cloud clusters, and orographic precipitation will be introduced. Examples of important deep-convection phenomena near the Taiwan area, such as typhoons and MCSs within a Mei-Yu front, and their associated dynamics will be demonstrated and discussed. Lecture Outline |
|
大氣海洋流體力學特論 |
郭鴻基 |
1 |
1. Conservation laws and basic equations: |
|
高等大氣動力學 |
郭鴻基 |
3 |
因應地球科學跨領域研究,高等大氣動力學課程的安排,除了傳統大氣動力學外,更廣泛包括大氣海洋流體力學 (Atmospheric Oceanic Fluid Dynamics, AOFD);課程也將加入新元素:例如探討空氣、水等流體性質對於生命科學與生物的影響;探討非線性動力數學建模,包含多重平衡與穩定、回饋、遲滯、同步、尺度分析等課題。課程重視數學思考與模式計算。 |
|
氣候診斷 |
盧孟明 / 隋中興 |
2 |
Climate predictions on weekly, monthly, seasonal and annual timescales involves many processes that operate among the atmosphere, ocean and land surface. Monitoring and analyzing the weekly to interannual climate variability is an efficient way to enhance our understanding of global and regional climate variability and the relationship with high-impact weather events. |
|
氣候變異與預測 |
盧孟明 |
3 |
氣候變異概指由大氣、海洋、陸表共同組成的氣候系統相對於三十年或更長時期平均狀態的偏離程度,重要現象有以週、月、季、年為時間單位的短期氣候變化,以及與其相依相存的年代(十年)、多年代、世紀等長週期緩慢變化。氣候變異的發生機制決定於大氣、海洋、陸表交互作用的過程,了解這些過程以及各主要變異模態對全球和區域氣候的影響是發展氣候預測的科學基礎。 |
|
熱帶氣候動力專題(1)-MJO |
盧孟明 |
1 |
This is an advanced Tropical Climate Dynamics course intended for graduate students. It will introduce key observational phenomena in tropics, and discuss dynamic mechanisms behind the observed phenomena. We plan to cover four topics (MJO, Monsoon, ENSO, Climate mean state) in successive four semesters. For this semester the special topic is MJO and the course outline is as following: |
|
熱帶氣候動力專題(2)-BSISO |
盧孟明 |
1 |
This is an advanced Tropical Climate Dynamics course intended for graduate students. It will introduce key observational phenomena in tropics, and discuss dynamic mechanisms behind the observed phenomena. We already covered the topic of MJO in 2018 Spring Semester and plan to continue covering four topics (BSISO, Monsoon, ENSO, Climate mean state) in successive four semesters. |
|
全球大氣環流 |
黃彥婷 |
3 |
This course introduces the characteristics and the associated mechanisms of the large-scale circulation in the atmosphere. With the goal of bridging theories and observation using conceptual and numerical models with different level of complexity, we focus on the zonal mean circulation and briefly extend to the 3D circulation. Topics include: Hadley Circulation, midlatitude zonal mean circulation, the interactions between tropics and extratropics, and 3D atmospheric circulation. The model-projected trend (during global warming) of these circulations will be covered by paper discussions, which are designed to review and discuss the fundamental theories and simplified models. |
|
雲動力學 |
吳健銘 |
3 |
This course focuses on the general dynamics of cloud systems. Models of fog, stratocumulus, shallow cumulus, deep cumulus, and orographic convection will be presented. Classes will include presentations by the instructor and students. Material covered in class will be supplemented by homework assignments, which require coding abilities. Numerical simulations of idealized convective systems will be conduced using the vector vorticity equation cloud resolving model (VVM). The class will conclude with student presentations on a chosen project based on the results of the numerical simulations. |
|
地球系統模式—物理過程 |
吳健銘 |
3 |
本課程將介紹地球系統模式之對流過程並分單元授課。主要介紹如何在大尺度模式中表示積雲對流的過程,將使用高解析大渦模式(LES),雲解析模式(CRM), 之模擬結果簡化成概念模式。課程內容包含講演與模式實作與分析。將分為下述課題: 乾對流過程、淺對流過程、深對流過程、大渦模式與雲解析模式之介紹 |
|
陸地大氣交互作用 |
羅敏輝 |
3 |
Feedbacks between land and atmosphere play a central role in the interactive functioning of the Earth's climate. The goal of this course is to understand the essential aspects of roles of land processes in the climate systems. Topics covered include: (1) basics of terrestrial surface energy, water and carbon balances, (2) ecohydrology, and (3) land use and land cover changes. Students will read several critical papers in these topics, and will also learn to design, perform, and analyze numerical climate experiments/outputs with a land surface model and climate model for their final project. |
|
中尺度氣象學 |
游政谷 |
2 |
隨著近年來觀測儀器(技術)的進步以及高解析度數值模式的廣泛應用,使得我們慢慢了解到,較劇烈且具傷害力的天氣現象(如強烈降水與風暴)常侷限於中小尺度的範疇。可是由於發生這些劇烈天氣的原因相當多樣化且複雜,傳統的綜觀氣象理論基礎已無法滿足我們對於這些現象的了解。本課程的主要目的為介紹實際大氣中的中尺度天氣現象,並就各種不同的中尺度天氣系統,廣泛說明它們內部的結構與隱含的物理與動力過程。這其中,現階段的了解為授課重心,然而目前最新的研究成果也會在課堂上適時予以補充說明。課程內容將針對下列主題作有系統的闡釋:(1)中尺度的基本概念 、(2)中尺度天氣現象的觀測分析與預報、(3)大氣對流的觀念、(4)中緯度及熱帶中尺度對流系統、(5)劇烈風暴、(6)鋒面的中尺度特徵與其伴隨的雨帶。 |
|
地物流力 |
陳世楠 / 林和 |
3 |
This is an upper-level undergraduate and graduate-level course on geophysical waves and instability. We will focus on slowly evolving flow that is nearly in geostrophic balance and thus satisfies the “Quasi-geostrophic (QG) approximation”. The primary subjects are: 1. QG The course format is a combination of lectures and student project, with student-led presentation/ discussion. |
|
雲與環境專題討論 |
陳維婷 |
3 |
本課程主旨在討論研究「台灣極端空氣汙染事件在不同天氣型態下之特性」,經由對觀測與模擬資料之分析瞭解當前東亞綜觀天氣型態下台灣PM2.5與環境條件、邊界層、雲物理、輻射收支、大尺度環流之關係,討論其中牽涉之物理過程,並推估未來氣候變遷情境下台灣PM2.5高汙染事件的可能改變。 |
|
氣候變遷科學 |
陳維婷 |
3 |
• This course provides a solid foundation in climate change science, including lectures on the physical basis of anthropogenic climate change, natural climate variations, and global climate models. Prerequisite on student levels: |
|
資料同化 |
連國淵 |
3 |
Data assimilation is an important field in numerical modeling and analysis in geoscience. It allows observation information to be objectively and optimally ingested into numerical models using statistical theories, providing analysis data which are essential for initializing model prediction and for climate studies. |
大學部選修
|
大學部選修 |
|||
|
課程名稱 |
教 師 |
學分 |
內 容 介 紹 |
|
動力氣候學 |
隋中興 |
3 |
本課程介紹大氣-海洋平均氣候與低頻震盪的特徵及動力過程,特別是熱帶多尺度波動。主要介紹ITCZ和年週期變化,熱帶氣旋與波動,季節內振盪、年際震盪(如厄爾尼諾 - 南方濤動,印度洋偶極子)、年代際變化。課程著重理論和概念模型的講授,以利學生理解觀測現象背後的物理機制。授課對象為具備大氣-海洋科學背景的大四及研究所學生。 |
|
大氣遙測 |
林依依 |
3 |
本課程將包含四大部分,分別為1.大氣輻射原理:介紹大氣的吸收、散射及發射等特性,其黑體輻射和大氣光譜之特性。2.大氣遙測原理:包括輻射傳送基本原理及衛星遙測的基本原理。3.衛星及其觀測頻道特性之介紹:氣象衛星與衛星遙測進展及技術演進之簡介,並探討衛星遙測頻道之特性、應用範圍、能力與限制,以及各種輻射計之簡介。4.大氣參數之反演及應用:衛星觀測資料在大氣遙測之應用,包括海面溫度、大氣垂直溫濕剖麵、氣膠、雲、降雨及海器參數等等之遙測。 |
|
氣候診斷 |
盧孟明 / 隋中興 |
2 |
Climate predictions on weekly, monthly, seasonal and annual timescales involves many processes that operate among the atmosphere, ocean and land surface. Monitoring and analyzing the weekly to interannual climate variability is an efficient way to enhance our understanding of global and regional climate variability and the relationship with high-impact weather events. |
|
大氣觀測實作 |
林博雄 |
2 |
為了落實教學實作精神,本課程利用本校生農學院梅峰山地農場為教學觀測場所,進行一週密集教學。授課內容包括:氣候變遷議題對生態環境的衝擊,人為開發環境和天然環境的微氣象差異,介紹各國對於森林環境監測的方法和工具,說明梅峰山地農場生物多樣性特色和局地氣候背景計畫。戶外觀測實作內容計有:地形雲與霧的觀察、雲霧酸鹼值測定、人工溫室與天然空曠地微氣象調查與差異分析、氣膠採樣分析 |
|
大尺度雲與水汽過程 |
隋中興 |
2 |
Earth atmosphere is uniquely regulated by water cycle. It spans wide spatiotemporal spectrum and many layers of governing physics. Through interactions with energy cycle and circulation, the moisture and cloud of highly fluctuating nature exhibit surprisingly coherent large-scale structure. The corresponding convective-radiative processes relevant in climate oscillations of different scales are essential part of climate dynamic. |
|
生物氣象學 |
林博雄 |
3 |
本課程探討大氣圈和生物圈的互動,針對動物、植物和人類等三大對象,探討生物氣象之理論與實務,最後討論氣候變遷對生態的衝擊議題。 |
|
全球大氣環流 |
黃彥婷 |
3 |
This course introduces the characteristics and the associated mechanisms of the large-scale circulation in the atmosphere. With the goal of bridging theories and observation using conceptual and numerical models with different level of complexity, we focus on the zonal mean circulation and briefly extend to the 3D circulation. Topics include: Hadley Circulation, midlatitude zonal mean circulation, the interactions between tropics and extratropics, and 3D atmospheric circulation. The model-projected trend (during global warming) of these circulations will be covered by paper discussions, which are designed to review and discuss the fundamental theories and simplified models. |
|
空氣汙染實作 |
洪惠敏 |
2 |
此課程提供學生基本空氣汙染知識及量測方法,並動手組裝小型量測儀器(Raspberry Pi single-board computer +高靈敏感測器),在期末將根據所此課程的知識及所組裝儀器進行校正及期末主題研究,根據監控化學物質時間及區域性分布探討汙染物的成因與影響。 |
|
生地化循環與氣候 |
洪惠敏 |
3 |
This course will discuss the interaction between biosphere, chemistry and climate from presentations with some hands-on-experiments. The contents of this course include: |
|
天氣診斷專題一 |
李清勝 / 楊明仁 |
2 |
本專題將利用中央氣象局所提供及其他可獲得之資料,對大氣內實際發生的現象,利用相關課程所學的學理進行診斷分析與詮釋;討論對象將包括不同尺度(行星尺度、綜觀尺度、中尺度、對流尺度)環流系統與天氣現象之結構與演變,並將特別注重區域性天氣現象有關之討論及詮釋。 |
|
高等數值天氣預報 |
楊明仁 |
3 |
This course will introduce the advanced applications of numerical weather prediction (NWP), mainly using the WRF model. The spectral and pseudospectral methods typically used in the global model and tropical cyclone studies will be discussed. Relaxation method used in solving the Laplace and Possion equations will be presented. Several methods for lateral boundaries used in regional models will be discussed. Class projects based on the material covered in this class will be assigned. Students taking this course are assumed to have the basic knowledge of finite-difference methods and numerical analysis. |
|
深對流特論 |
楊明仁 |
3 |
The physical and dynamical processes of deep cumulus clouds, which usually occur in mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), tropical cyclones and cloud clusters, and orographic precipitation will be introduced. Examples of important deep-convection phenomena near the Taiwan area, such as typhoons and MCSs within a Mei-Yu front, and their associated dynamics will be demonstrated and discussed. Lecture Outline |
|
大氣海洋流體力學特論 |
郭鴻基 |
1 |
1. Conservation laws and basic equations: |
|
高等大氣動力學 |
郭鴻基 |
3 |
因應地球科學跨領域研究,高等大氣動力學課程的安排,除了傳統大氣動力學外,更廣泛包括大氣海洋流體力學 (Atmospheric Oceanic Fluid Dynamics, AOFD);課程也將加入新元素:例如探討空氣、水等流體性質對於生命科學與生物的影響;探討非線性動力數學建模,包含多重平衡與穩定、回饋、遲滯、同步、尺度分析等課題。課程重視數學思考與模式計算。 |
|
氣候變異與預測 |
盧孟明 |
3 |
氣候變異概指由大氣、海洋、陸表共同組成的氣候系統相對於三十年或更長時期平均狀態的偏離程度,重要現象有以週、月、季、年為時間單位的短期氣候變化,以及與其相依相存的年代(十年)、多年代、世紀等長週期緩慢變化。氣候變異的發生機制決定於大氣、海洋、陸表交互作用的過程,了解這些過程以及各主要變異模態對全球和區域氣候的影響是發展氣候預測的科學基礎。 |
|
熱帶氣候動力專題(1)-MJO |
盧孟明 |
1 |
This is an advanced Tropical Climate Dynamics course intended for graduate students. It will introduce key observational phenomena in tropics, and discuss dynamic mechanisms behind the observed phenomena. We plan to cover four topics (MJO, Monsoon, ENSO, Climate mean state) in successive four semesters. For this semester the special topic is MJO and the course outline is as following: |
|
熱帶氣候動力專題(2)-BSISO |
盧孟明 |
1 |
This is an advanced Tropical Climate Dynamics course intended for graduate students. It will introduce key observational phenomena in tropics, and discuss dynamic mechanisms behind the observed phenomena. We already covered the topic of MJO in 2018 Spring Semester and plan to continue covering four topics (BSISO, Monsoon, ENSO, Climate mean state) in successive four semesters. |
|
R程式語言及其在大氣模式資料分析的應用 |
盧孟明 |
1 |
This course is to provide students a basic understanding of R programing. We will first introduce software installation and configuration for a statistical programming environment and generic programming concepts. Then we will cover practical issues in statistical analysis for weather forecast model data. |
|
大氣觀測實作(二) |
林博雄 |
2 |
本課程延伸「大氣測計學」必修課程,透過本系教學觀測設備(小型風力發電機太陽能光電電池等套件),在觀測坪戶外組裝並分析即時風場與太陽能輻射觀測資料,來實際診斷氣象與綠色能源的關聯與累積實作經驗;此外, 也配合本系教師所接受的政府委託計畫之相關戶外氣象觀測活動,進行密集式觀測實作,讓修課學生體驗氣象資料蒐集過程和可能面對的戶外環境挑戰,以及原始資料後端處理程序。 |
|
雲動力學 |
吳健銘 |
3 |
This course focuses on the general dynamics of cloud systems. Models of fog, stratocumulus, shallow cumulus, deep cumulus, and orographic convection will be presented. Classes will include presentations by the instructor and students. Material covered in class will be supplemented by homework assignments, which require coding abilities. Numerical simulations of idealized convective systems will be conduced using the vector vorticity equation cloud resolving model (VVM). The class will conclude with student presentations on a chosen project based on the results of the numerical simulations. |
|
地球系統模式—物理過程 |
吳健銘 |
3 |
本課程將介紹地球系統模式之對流過程並分單元授課。主要介紹如何在大尺度模式中表示積雲對流的過程,將使用高解析大渦模式(LES),雲解析模式(CRM), 之模擬結果簡化成概念模式。課程內容包含講演與模式實作與分析。將分為下述課題: 乾對流過程、淺對流過程、深對流過程、大渦模式與雲解析模式之介紹 |
|
陸地大氣交互作用 |
羅敏輝 |
3 |
Feedbacks between land and atmosphere play a central role in the interactive functioning of the Earth's climate. The goal of this course is to understand the essential aspects of roles of land processes in the climate systems. Topics covered include: (1) basics of terrestrial surface energy, water and carbon balances, (2) ecohydrology, and (3) land use and land cover changes. Students will read several critical papers in these topics, and will also learn to design, perform, and analyze numerical climate experiments/outputs with a land surface model and climate model for their final project. |
|
中尺度氣象學 |
游政谷 |
2 |
隨著近年來觀測儀器(技術)的進步以及高解析度數值模式的廣泛應用,使得我們慢慢了解到,較劇烈且具傷害力的天氣現象(如強烈降水與風暴)常侷限於中小尺度的範疇。可是由於發生這些劇烈天氣的原因相當多樣化且複雜,傳統的綜觀氣象理論基礎已無法滿足我們對於這些現象的了解。本課程的主要目的為介紹實際大氣中的中尺度天氣現象,並就各種不同的中尺度天氣系統,廣泛說明它們內部的結構與隱含的物理與動力過程。這其中,現階段的了解為授課重心,然而目前最新的研究成果也會在課堂上適時予以補充說明。課程內容將針對下列主題作有系統的闡釋:(1)中尺度的基本概念 、(2)中尺度天氣現象的觀測分析與預報、(3)大氣對流的觀念、(4)中緯度及熱帶中尺度對流系統、(5)劇烈風暴、(6)鋒面的中尺度特徵與其伴隨的雨帶。 |
|
地物流力 |
陳世楠 / 林和 |
3 |
This is an upper-level undergraduate and graduate-level course on geophysical waves and instability. We will focus on slowly evolving flow that is nearly in geostrophic balance and thus satisfies the “Quasi-geostrophic (QG) approximation”. The primary subjects are: 1. QG The course format is a combination of lectures and student project, with student-led presentation/ discussion. |
|
雲與環境專題討論 |
陳維婷 |
3 |
本課程主旨在研究「冬季風環境下近海對流」之特性及其在天氣與氣候中之重要性。 |
|
氣候變遷科學 |
陳維婷 |
3 |
• This course provides a solid foundation in climate change science, including lectures on the physical basis of anthropogenic climate change, natural climate variations, and global climate models. Prerequisite on student levels: |
|
大氣科學研究導論 |
各教師 |
2 |
介紹大氣科學的研究內容、方法、成果及展望。課程依本系之主要學程/領域,即天氣動力領域、氣候系統領域、大氣環境領域、大氣資訊領域等四大領域相關研究進行介紹,以使學生對於大氣科學整體研究之現況及展望,有宏觀及較深入之了解,並作為學生未來選擇大氣科學研究之參考。本課程定位為大四所開”獨立研究”之先修課程,由本系各不同專長之教授合開,並將透過學生與相關授課老師之互動,提昇學生對於大氣科學各面相主流研究與應用之認知與興趣。 |
|
獨立研究 |
各教師 |
2 |
由各指導老師應學生要求,針對學生在大氣科學某方面之興趣,指導學生從事研究、撰寫讀書報告。 |
|
學士論文 |
各教師 |
2 |
由各指導老師應學生要求,針對學生在大氣科學某方面之興趣,指導學生從事研究撰寫正式論文。 |



